Inorganic Chemistry MCQ on Atomic Structure
Inorganic Chemistry MCQ on Atomic Structure
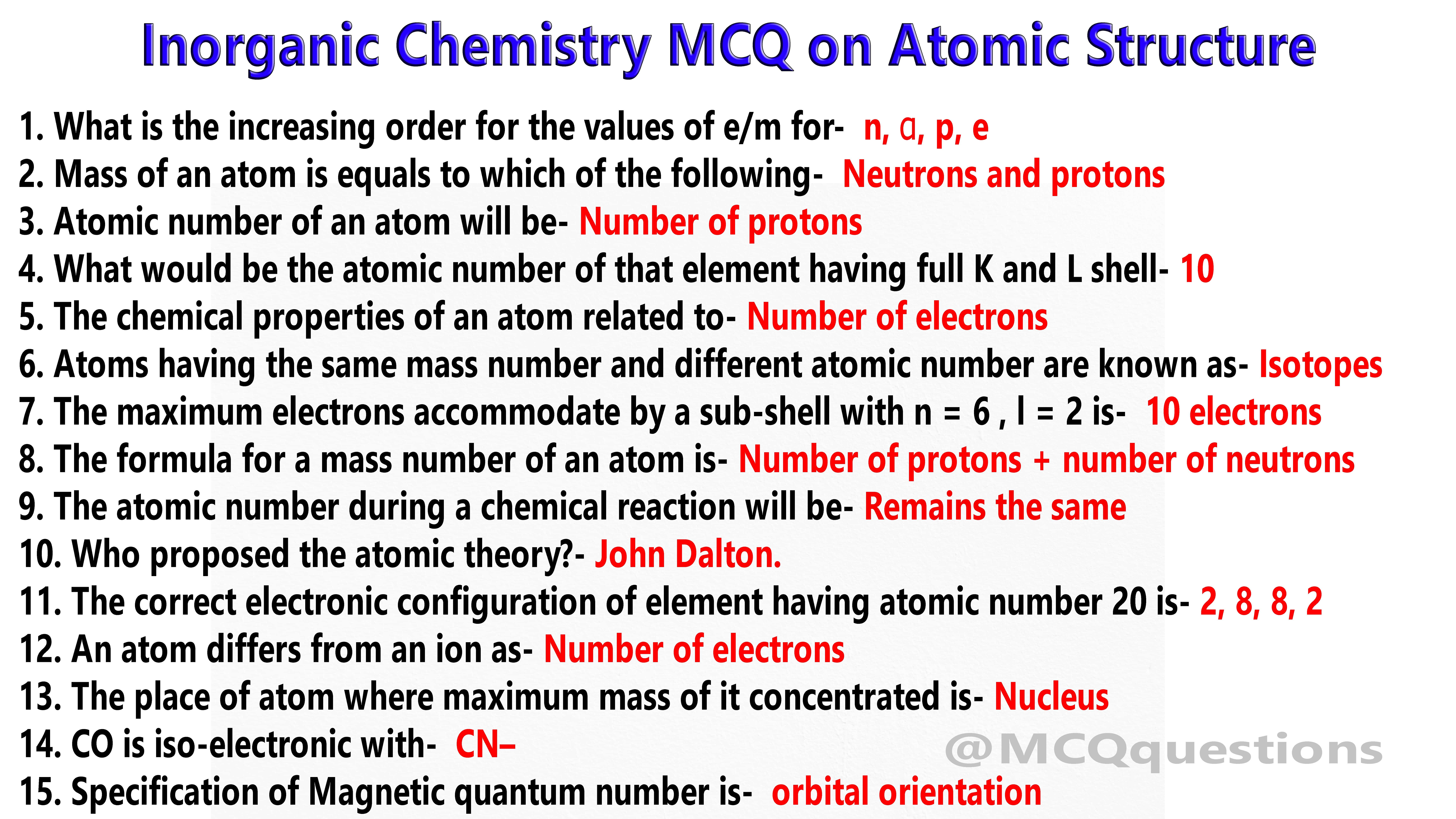
1. What is the increasing order for the values of e/m for
(a) e, p, n, α
(b) n, p, e, α
(c) n, p, α, e
(d) n, α, p, e
Answer - (d) n, α, p, e
2. Mass of an atom is equals to which of the following
(a)Only protons.
(b)Only neutrons.
(c)Neutrons and protons.
(d)Protons and electrons.
Answer -(c)Neutrons and protons.
3. Atomic number of an atom will be
(a)Number of electrons.
(b)Number of protons.
(c)Number of electrons and protons.
(d)Number of protons and neutrons.
Answer -(b)Number of protons.
4. Nickel has atomic number 28. The correct electronic configuration is
(a)1s2 2s2 2p4 3s2 3p8 3d10
(b)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2
(c)1s2 2s2 2p4 3s2 3p6 4s2
(d)1s2 2s2 3s2 3p8 3d10
Answer -(b)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2
5. What would be the atomic number of that element having full K and L shell
(a)20
(b)14
(c)10
(d)16
Answer -(c)10
6. The chemical properties of an atom related to
(a)Number of protons.
(b)Number of electrons.
(c)Number of neutrons.
(d)None of these.
Answer -(b)Number of electrons.
7. Atoms having the same mass number and different atomic number are known as
(a)Isotopes.
(b)Isotones.
(c)Isobars.
(d)Isomers.
Answer -(a)Isotopes.
8. Which of the following quantum number helps to distinguish the electrons of the same orbitals ?
(a) Principal quantum number
(b) Azimuthal quantum number
(c) Magnetic quantum number
(d) Spin quantum number
Answer -(d) Spin quantum number
9. The maximum electrons accommodate by a sub-shell with n = 6 , l = 2 is
(a) 12 electrons
(b) 10 electrons
(c) 36 electrons
(d) 72 electrons
Answer -(b) 10 electrons
10. Given that the ionization enthalpy of hydrogen atom is 1.312 × 106 J mol-1. Then the required amount of energy for the excitation of the electron in the atom from n = 1 to n = 2 is
(a) 8.51 × 105 J mol-1
(b) 6.56 × 105 J mol-1
(c) 7.56 × 105 J mol-1
(d) 9.84 × 105 J mol-1
Answer-(d) 9.84 × 105 J mol-1
11. The formula for a mass number of an atom is
(a)Number of protons + number of electrons.
(b)Number of neutrons + number of electrons.
(c)Number of protons + number of neutrons.
(d) Non of these
Answer -(c)Number of protons + number of neutrons.
12. The atomic number during a chemical reaction will be
(a)Increases.
(b)Changes.
(c)Remains the same.
(d)Changes alternatively.
Answer -(c)Remains the same.
13. Who proposed the atomic theory?
(a)John Dalton.
(b)Robert Millikan.
(c)J. J. Thomson.
(d)Neils Bohr.
Answer -(a)John Dalton.
14. The correct electronic configuration of element having atomic number 20 is
(a)2, 6, 6, 2
(b)2, 8, 8, 2
(c)2, 4, 6, 2
(d)2, 4, 6, 2
Answer -(b)2, 8, 8, 2
15. An atom differs from an ion as
(a)Number of protons.
(b)Nuclear charge.
(c)Number of electrons.
(d)Mass number.
Answer -(c)Number of electrons.
16. The place of atom where maximum mass of it concentrated is
(a)Nucleus.
(b)Neutrons.
(C)Protons.
(d)Electrons.
Answer -(a)Nucleus.
17. CO is iso-electronic with
(a) O–2
(b) N+2
(c) CN–
(d) O+2
Answer -(c) CN–
18. Which of the following corresponds to the line spectrum of hydrogen obtained in the visible region of light?
(a) Lyman series
(b) Balmer series
(c) Paschen series
(d) Brackett series
Answer -(b) Balmer series
19. Which of following will be isolates, If the nitrogen atom had electronic configuration 1s², it would have energy lower than that of the normal ground state configuration 1s² 2s² 2p³, as the distance between electrons and the nucleus is too less. Yet, 1s² is not observed.
(a) Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle
(b) Hund’s rule
(c) Pauli Exclusion Principle
(d) Bohr postulate of stationary orbits
Answer-(c) Pauli Exclusion Principle
20. if the quantum numbers + 1/2 and – 1/2 for the electron spin it resembles
(a) rotation is clockwise and anticlockwise direction respectively
(b) rotation is anticlockwise and clockwise direction respectively
(c) m Is up and down respectively
(d) 2 quantum mechanical spin states which have no classified analogue
Answer -(d) 2 quantum mechanical spin states which have no classified analogue
21. What will be the possible energy value of the excited state for electron in Bohr orbitals of hydrogen is ,
(Given energy of electron in the first Bohr orbit of H atom is 13.6 eV.)
(a) – 3.4 eV
(b) -4.2eV
(c) – 6.8 eV
(d) + 6.8 eV
Answer-(a) – 3.4 eV
22. What will be the atomic number of the element , if the last entering electron in an element has quantum number n = 3, l = 2, m = + 2 and s = + 1 /2.
(a) 13
(b) 21
(c) 29
(d) 39
Answer- (c) 29
23. Given energy = 2.91 × 10-19], h = 6.36 × 10-34 Js, c = 3.0 × 108 m/s ,Then what will be the wavelength of light?
(a) 6.56 nm
(b) 656 nm
(c) 0.656 nm
(d) 65.6 nm
Answer- (b) 656 nm
24. Which of the following statement is explained by Bohr’s atomic model?
(a) the spectrum of hydrogen atom only
(b) The spectrum of an atom/ion having only one electron.
(c) the spectrum of hydrogen molecule
(d) the solar spectrum
Answer- (b) The spectrum of an atom/ion having only one electron.
25. Specification of Magnetic quantum number is
(a) orbital size
(b) orbital shape
(c) orbital orientation
(d) nuclear stability
Answer- (c) orbital orientation
26. Accurate set of quantum numbers belong to highest energy is
(a) n = 4, l = 0, m = 0, s = + 12
(b) n = 3, l = 0, m = 0, s = + 12
(c) n = 2, l = 1, m = 1, s = + 12
(d) n = 3, l = 2, m = 1, s = + 12
Answer- (d) n = 3, l = 2, m = 1, s = + 12
27. Write The correct sequence to label the subshells in an atom is
(a)S, p, d, f, g
(b)S, p, p, f, d
(c)S, s, p, p, d, f, g
(d)S, p, g, d, f
Answer - (a)S, p, d, f, g
28. Which rule will this configuration be violating,if electronic configuration for oxygen is written as 1s2 2s2 2p4.
(a)Aufbau’s principle.
(b)Hund’s rule.
(c)Pauli’s exclusion principle.
(d)None of the above.
Answer (d)None of the above.
29. If an atom has four unpaired electrons. Then total spin of electron is
(a)1
(b)2.5
(c)2
(d)4
Answer (c)2
30. The charge and mass ratio of cathod rays resembles to
(a) a-particles
(b) anode rays
(c) B-rays
(d) protons.
Answer (c) B-rays
31.The nucleus of an atom has
(a) protons and neutrons.
(b) protons and electrons
(c) neutrons and electrons.
(d) protons, neutrons and electrons.
Answer (a) protons and neutrons.
32. Generally Cathode rays are known as
(a) protons
(b) electrons
(c) neutrons
(d) a-particles
Answer (b) electrons
33. Proton may be defined as
(a) an ionised hydrogen molecule
(b) an alpha-ray particle
(c) a fundamental particle
(d) nucleus of heavy hydrogen
Answer (c) a fundamental particle
34. The order of size of nucleus ia
(a) 10-⁸cm
(b) 10-¹³cm
(c) 10-¹⁰cm
(d) 10-¹⁸ cm.
Answer (b) 10-¹³cm
35. The electron having a mass of
(a) 9.11 × 10-²⁷ g
(b) 9.11 × 10-²³ g
(c) 9.11 x 10-²⁸g
(d) 9.11 × 10-³⁸ g.
Answer (c) 9.11 x 10-²⁸g
36. The charge on proton is
(a) 1.602 10-19 C
(b) 1.502 10-19 C
(c) 1.602 10-20 C
(d) 1.502 10-21 C.
Answer (a) 1.602 10-19 C
37. The average distance of electron from the nucleus within an atom is equals to the order of
(a) I cm
(b) 10¹³cm
(c) 10-⁸cm
(d) 10-¹²cm.
Answer (c) 10-⁸cm
38. The founder of anode rays
(a) Crookes
(b) Goldstein
(c) Thomson
(d) Chadwick.
Answer (b) Goldstein
39.The Canal rays are known as
(a) electrons
(b) neutrons
(c) protons
(d) positively charged ions.
Answer (d) positively charged ions.
40. Except which of the following, neutrons are
present in all atoms?
(a) H
(b) Ar
(c) He
(d) Ne
Answer (a) H
41. Cl (34,17)and Cl (37,17)differ from each other in number of
(a) nucleon
(b) positrons
(c) protons
(d) electrons.
Answer (a) nucleon
42. Isotones are those which have same
(a) atomic number
(b) mass number
(c) number of neutrons
(d) number of electrons.
Answer (c) number of neutrons
43. An isotone of Ge(76,32) is
(a) Ge(77,32)
(b) Kr (81,36)
(c) Se(77,34)
(d) As(77,33)
Answer (d) As(77,33)
44. The non-integral atomic masses having by many elements is due to
(a) they have isobars
(b) their isotopes have non-integral masses
(c) their isotopes have different masses
(d) the constituents, neutrons, protons and electrons. combine to give fractional masses.
Answer (c) their isotopes have different masses
45. The number of electrons in an atom is same as its
(a) atomic weight
(b) atomic number
(c) equivalent weight
(d) electron affinity.
Answer (b) atomic number
46. Neon iso-electronic with
(a) O
(b) Mg²+
(c) N-
(d) F-²
Answer (b) Mg²+
47. What is the ratio of charge to mass that was determined by J.J Thomson (in coulombs per gram)
(a) -1.76 10⁸coulombs/ g
(b) 1.76 10-⁸ coulombs/g
(c) -1.76x 10¹⁰ coulombs/g
(d) -1.76×10-¹⁰ coulombs /g.
Answer (a) -1.76 10⁸coulombs/ g
48. Rutherford’s scattering experiment explains about
(a) the size nucleus
(b) size electron
(c) radius of atom
(d) radius neutron
Answer (a) the size nucleus
49. According to Rutherford’s theory, which of the following statement is not true?
(a) alpha particles going near the nucleus are slightly deflected
(b) some of alpha -particles pass through the nucleus
(c) Most of the bita-particles pass through without deflection
(d) A few alpha particles are deflected back
Answer (b) some of alpha -particles pass through the nucleus
50. The mass of a neutron is
(a) same as that of a proton
(b) slightly less than proton
(c) slightly more than a proton
(d) same as that of an electron.
Answer (c) slightly more than a proton
51. Rutherford’s experiment of a particles showed for the first time that atom has
(a) nucleus
(b) electrons
(c) protons
(d) neutrons
Answer (a) nucleus
52. Which established the nuclear model of the atom used a beam of(basis of Rutherford’s theory)
(a) bita-particles, which impinged on a metal foil .
(b) Bita-rays, which impinged on a metal foil and ejected electron
(c) helium atoms, which impinged on a metal foil andst scallered
(d) helium nuclei, which impinged on a metal fail and got scallerod
Answer (d) helium nuclei, which impinged on a metal fail and got scallerod
MCQ on Quantum Numbers
1. For l = 1, the shape of the orbital is
(a) Unsymmetrical
(b) Spherically symmetrical
(c) Dumb-bell
(d) Complicated
Answer. (c) Dumb-bell
2. The principal quantum number represents
(a) Shape of an orbital
(b) Distance of electron from nucleus
(c) Number of electrons in an orbit
(d) Number of orbitals in an orbit
Answer. (b) Distance of electron from nucleus
3. How many electrons can be fit into the orbitals that comprise the 3rd energy level ?
(a) 2
(b) 8
(c) 18
(d) 32
Answer. (c) 18
4. If value of l = 0, the shape of the orbital is
(a) Rectangular
(b) Spherical
(c) Dumbbell
(d) Unsymmetrical
Answer. (b) Spherical
5. For n = 3, the number of possible orbitals are
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 9
Answer. (d) 9
6.When 3d orbital is complete, the new electron will enter the
(a) 4p-orbital
(b) 4f-orbital
(c) 4s-orbital
(d) 4d-orbital
Answer. (a) 4p-orbital
7. Total number of radial nodes of 3s and 2p orbitals are respectively.
(a) 2, 0
(b) 0, 2
(c) 1, 2
(d) 2, 1
Answer. (a) 2, 0
8. The mvr of an electron depends on
(a) Principal quantum number
(b) Azimuthal quantum number
(c) Magnetic quantum number
(d) All of these
Answer. (b) Azimuthal quantum number
9. The maximum energy is present in any electron at which area
(a) Nucleus
(b) Ground state
(c) First excited state
(d) Infinite distance from the nucleus
Answer. (d) Infinite distance from the nucleus
10.The number of orbitals for n = 4 will be
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 12
(d) 16
Answer. (d) 16
11.The two electrons in K sub-shell will differ in
(a) n
(b) l
(c) m
(d) s
Answer. (d) s
12.The element having atomic number 29 possess how many unpaired electrons in
d-orbitals
(a) 10
(b) 1
(c) 0
(d) 5
Answer. (c) 0
13. The similarities found between 2p and 3p orbital that is
(a) Shape
(b) Size
(c) Energy
(d) Value of n
Answer. (a) Shape
14. The azimuthal quantum number is related to
(a) Size
(b) Shape
(c) Orientation
(d) Spin
Answer. (b) Shape
15.Value of l for last electron of Na atom is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 0
Answer. (d) 0
16. In d orbitals the maximum number of unpaired electron can be present is
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 7
Answer. (c) 5
17. The number of unpaired electrons in an O2 molecule is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer. (c) 2
18.The number of unpaired electron I the element for Z=29
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 2
Answer. (a) 1
19. Maximum how many quantum numbers may same by two electrons
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer. (c) Three
20. How many orbitals can have the following quantum numbers, n = 3, l = 1, ml = 0?
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 3
Answer: (c) 1
21. For the set of quantum numbers, n = 3, l = 1, m = -1, the maximum electrons will be
(a) 2
(b) 6
(c) 10
(d) 4
Answer: (a) 2
22. The maximum number of electrons that can fit in an orbital with n = 3 and l = 1?
(a) 14
(b) 6
(c) 10
(d) 2
Answer: (d) 2
23. Which of the following helps to determine the maximum number of electrons present in a subshell
(a) 2l + 1
(b) 2n2
(c) 4l + 2
(d) 4l – 2
Answer: (c) 4l + 2
24. Which of the following quantum numbers governs the spatial orientation of an atomic orbital?
(a) Magnetic quantum number
(b) Spin quantum number
(c) Azimuthal quantum number
(d) Principal quantum number
Answer: (a) Magnetic quantum number
25. Which one represents the three-dimensional shape of an atomic orbital
(a) Azimuthal quantum number
(b) Principal quantum number
(c) Spin quantum number
(d) Magnetic quantum number
Answer: (a) Azimuthal quantum number
26. The maximum number of orbitals present in a subshell can be represented by
(a) 2l + 1
(b) 2n2
(c) 4l + 2
(d) 4l – 2
Answer: (a) 2l + 1
27. For the orbitals with n = 2 and l = 1, the number of electrons that fit in it is
(a) 8
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 4
Answer: (c) 6
28. For l=3 the number of electrons will be
(a) 14
(b) 2
(c) 10
(d) 6
Answer: (a) 14
Also You Can Read Inorganic Chemistry MCQ
